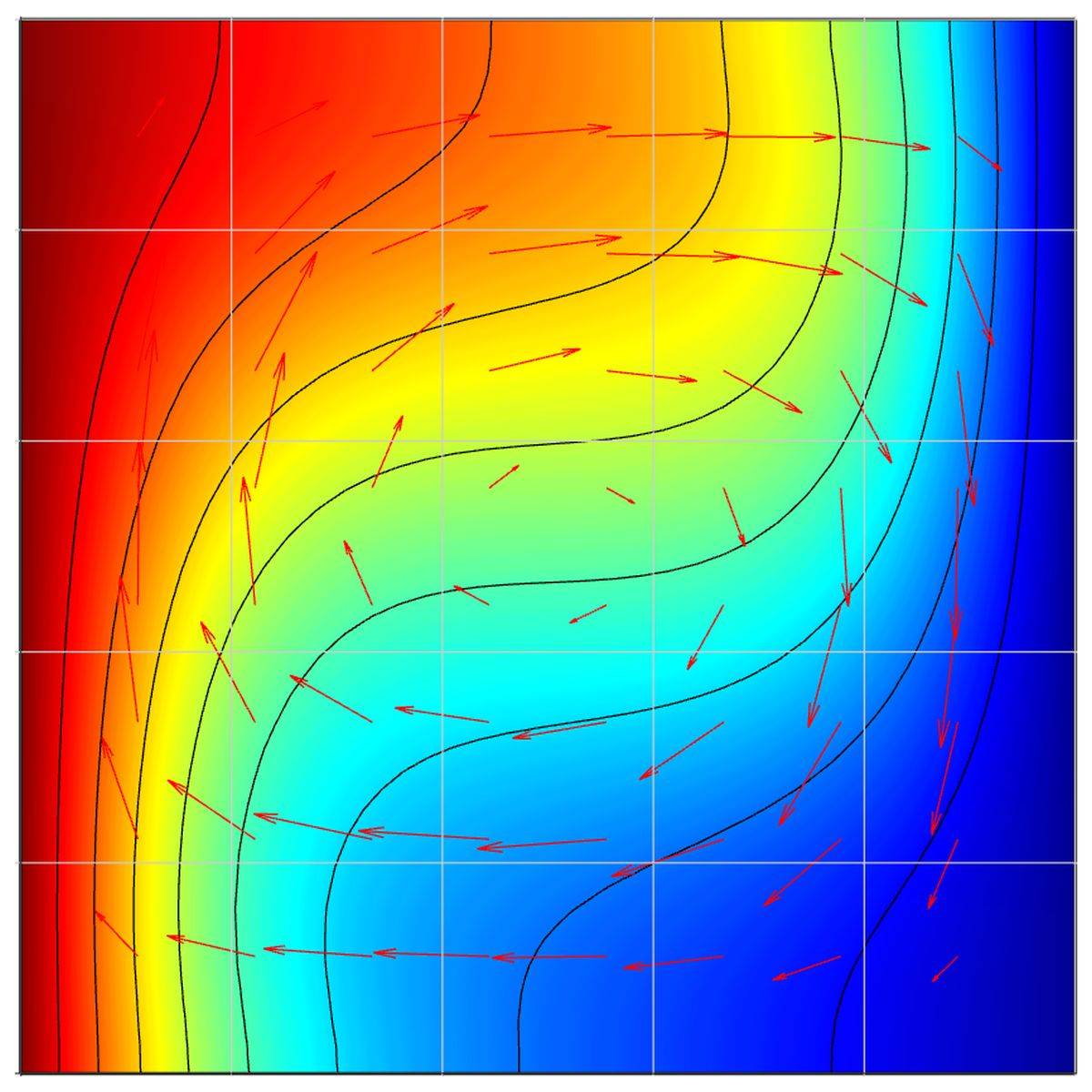
This multiphysics model illustrates natural convection effects in a unit square domain using the Boussinesq approximation. The model involves a Navier-Stokes equations physics mode, representing the fluid flow with solid wall or no-slip boundary conditions everywhere. In addition a heat transfer physics mode is added to model the temperature field . The top and bottom boundaries are perfectly insulated while the left boundary is prescribed a unit temperature and the right zero.
The physics modes are two way coupled through the vertical source term in the Navier-Stokes equations, Pr·Ra·T, and the velocities transporting the temperature coming directly from the fluid flow. First, the Prandtl and Rayleigh numbers are set to Pr = 0.71 and Ra = 103, respectively, after which the Ra number will be increased to 104. The references contain benchmark reference and comparison results for a number of quantities such as maximum velocities and the Nusselt number [1,2].
This model is available as an automated tutorial by selecting Model Examples and Tutorials… > Multiphysics > Natural Convection in a Square Cavity from the File menu, and also as the MATLAB simulation m-script example ex_natural_convection. Step-by-step tutorial instructions to set up and run this model are linked below.
References
[1] D. de Vahl Davis, Natural Convection of Air in a Square Cavity - A Benchmark Solution, Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids, vol. 3, pp. 249-264, 1983.
[2] D. de Vahl Davis and I. P. Jones, Natural Convection of Air in a Square Cavity - A Comparison Exercise, Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids, vol. 3, pp. 227-248, 1983.